Feature Story Accelerating digital transformation of shipyards through technology qu…
페이지 정보
작성자 최고관리자 댓글 0건 조회 3,112회 작성일 23-09-15 12:36본문
- Use of new approaches require shipbuilders, end users and class to be satisfied that risks are understood and managed, writes Gareth Burton, VP, Global Technology, ABS
The use of new technologies is driving shipyard production into new, exciting and sometimes unfamiliar frontiers, expanding across the use of technology such as AR/VR, 3D plan review, simulation and modelling, digital twins and other tools. The increasing application of such digital processes, including the certification of new technologies, can be supported by class.
The need to drive safety and quality as part of this technology revolution creates a demand among vessel designers and shipyards for validation and certification of digital processes. It also enables class and yards to better co-ordinate their workstreams, potentially changing the physical touchpoints during construction and providing the standards for data flows that support digital class and remote technology during a vessel’s operational life.
Qualification of technology during construction builds a set of standards and a framework that allows class to collect more of the key data that promotes not just next level efficiency but safety too. Fundamental to this approach is class guidance which introduces the process to recognise shipyards utilising and incorporating smart technologies into their operational processes.
Examples include the pioneering work by ABS and Seatrium integrating smart functions into the world’s first smart LNG bunkering vessel FueLNG Bellina, equipped with Seatrium’s proprietary AssetCare Digital Solution. The same philosophy powers a joint development project between ABS and Nakilat-Keppel Offshore & Marine Ltd examining how remote survey of vessels in service can be applied to surveys and inspections in the shipyard.
To help more shipyards understand how to embrace smart technologies, the ABS Guide, Smart Technologies for Shipyards lays out a Smart Technology Certification Framework, providing guidelines for shipyards to demonstrate the integration of qualified Smart Technology into their operational processes.
Qualification Process Overview
One of the challenges faced by industries undergoing digital transformation is that technologies often develop faster than the codes or regulations that govern them. In many cases, new technologies have little or no precedent in their target application and may drastically alter the way a certain process or activity has been done for decades. The lack of service history and successful real-world demonstrations raises questions about the technology’s readiness, maturity, and safety.
The qualification process addresses these concerns by demonstrating to potential end-users(and the industry as a whole) that all risks associated with the technology’s implementation have been systematically reviewed and maturity has been verified.
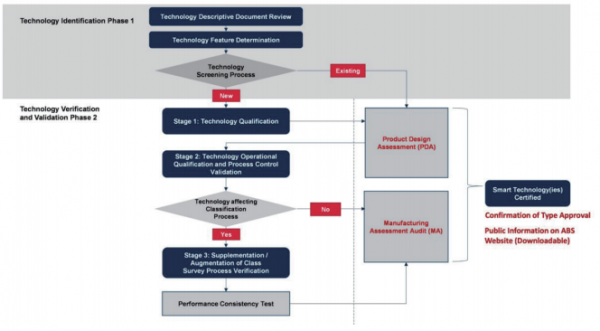
ABS’ Technology Qualification process included in the Smart Technology Guidance confirms the ability of a new or existing technology to perform its intended functions in accordance with defined performance requirements. The process starts with a comprehensive description of the technology to be qualified, followed by a screening of the technology to reveal the new or novel features that the qualification should focus on.
The process is divided into five sequential stages that progressively qualify the technology from feasible to operational stages. These stages span feasibility, concept verification, prototype validation, system integration and operations.
The qualification activities within each stage revolve around risk assessments and engineering evaluations that build upon each other to determine if the technology provides acceptable levels of safety in line with current shipyard industry practice. The qualification efforts by all stakeholders such as the vendor, system integrator, and end-user at each stage are recognised and captured within the qualification process.
Upon completion, eligible technologies can be Type Approved by ABS to limit repeated evaluation of identical designs. When all engineering evaluations are complete, a Product Design Assessment(PDA) can be issued prior to further consideration for Type Approval.
The Certification Framework
The Confirmation of Type Approval process shown in Figure 1 demonstrates that all software, related hardware quality assurance and control systems incorporated in the technology have been reviewed for compliance with one or more ABS Rules or Guides, statutory, industrial or manufacturer’s standards or other criteria acceptable to ABS.
Technology Qualification is just the first phase in the overall certification process. The second phase is Technology Operational Qualification and Process Control Validation, equivalent to design validation and quality management assessment, issuance of Manufacturing Assessment(MA) and Type Approval Certification for the technology used for non-Class related activities.
For shipyard technologies that will be used for non-Class related activities, upon successful completion of the first and second phases, the technology is eligible for a Confirmation of Type Approval – Tier 3. This certificate is available when a valid PDA - Tier 2 and a valid MA – Tier 3 remain current. The Type Approval certifies that the implementation of the technology complies with a recognised standard, at least to ISO9000 series or equivalent. Equivalency will ultimately be determined by ABS on a case-by-case basis.
For shipyard technologies that will be used as part of the Classification process (i.e., to supplement, augment or complement tasks that are related to or affecting the Classification process in ship construction, repair, or commissioning activities) an additional step/third stage is required known as Supplementation/Augmentation of Class Survey Process. The purpose of this stage is to make sure that the qualified process using the technology can produce results that are the same or better than the traditional process or approach.
Accelerating the Transition to Smart Shipyards
Digitalisation of shipyards continues to accelerate as builders seek to capitalise on technologies that can help them improve design and fabrication, and enhance operational health and safety. The implementation of these smart technologies can enable new and more efficient ways of working providing that the risks they present can be identified and mitigated.
Qualification and/or certification of technologies by an independent third-party has played an important role in the digital transformation of other industries, including the shipping and offshore sectors. It demonstrates a level of feasibility and maturity in order to gain a competitive advantage with customers, partners, and other stakeholders.
Additionally it provides regulatory agencies with confidence that any hazards and/or risks associated with the introduction of the proposed technology have been systematically reviewed and that appropriate mitigation measures have been put in place.
This combination of technology assessment and regulatory oversight provides tangible dividends for shipyards keen to improve their performance and shipowners looking to manage the safety of transition technologies.
It is clear that new technologies and the increased use of data can support sustainability as well as creating efficiencies; they can also help class and owner optimise the survey process – during construction and afterwards, leveraging technology beyond asset production and in support of the class process.
■ Contact: ABS www.eagle.org












