Feature Story Current Development Status of Russia’s Shipbuilding Industry
페이지 정보
작성자 최고관리자 댓글 0건 조회 3,343회 작성일 19-05-29 15:24본문
1. Overview
Russia’s shipbuilding industry is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate(CAGR) of 6% for 2015-2020. Russia’s shipbuilding industry has grown rapidly as the government-led programs to promote replacement of imported marine equipment and the development of the Arctic route began in full scale from 2016. Russian government expects an increase in domestic productivity of equipment by 2018 with completion of the import substitution program.
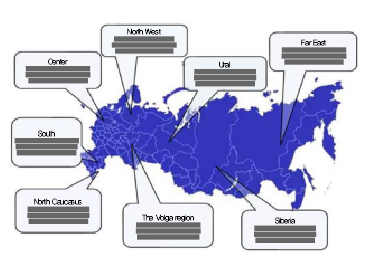
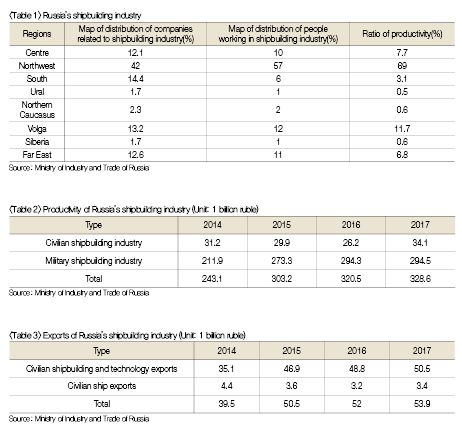
Meanwhile, there has been delay in the expansion of domestic equipment production under the import substitution program in the Russian shipbuilding industry due to sluggish investment in shipbuilding industry and aging of shipbuilding facilities. There are a total of 170 companies related to shipbuilding industry in Russia, which are concentrated mainly in the northwestern region. In Russia, shipbuilding industry employs about 170,000 persons. Most companies are affiliated with the United Shipbuilding Corporation(USC). USC member companies are generating more than 60% of sales in Russia’s shipbuilding industry. The modernization of Zvezda shipyard in the Far East(Bolshoy Kamen coast) began in 2016, led by Russian government(USD 2.5 billion budget). When the modernization is completed by 2024, Zvezda shipyard expected to become the largest shipyard in Russia. There are a total of 127 research institutes related to shipbuilding industry in Russia, out of which more than one third(1/3) are located in the northwestern region and some are scattered in the Volga, Central and Far East regions.
Meanwhile, the Crimean Peninsula, annexed by the Russian Federation in 2014, is home to 13 shipbuilding industry-related companies.
Russian shipbuilding industry can be divided at large into civilian segment and military segment.
Military shipbuilding segment’s productivity accounts for more than 90% of the total productivity. More than 90% facility and equipment produced in Russia’s shipbuilding industry are military applications(USD 5 billion, as of 2017). The entire Russian market is worth about USD 5.66 billion.
Exports related to Russia’s shipbuilding industry amount to approximately USD 930 million each year with military shipbuilding and technology exports worth about USD 870 million.
There are about 170 companies involved in Russian shipbuilding industry, out of which 43 are the shipbuilding research and design offices. Of the 127 companies directly involved in the shipbuilding industry of Russia, 45% are engaged in remodeling and repairing old vessels; 14% are electrical and engineering companies; 28% are parts and equipment-related companies; and 13% are service-related companies. Of the 43 shipbuilding research and design offices, 44% are involved in ship remodeling and repair; 40% are related to facilities and equipment; 14% are related to services; and electricity and engineering-related companies account for only 2%.
Russian shipbuilding industry achieved remarkable growth in 2016, and particularly, the civilian sector shipbuilding productivity was increased drastically. In 2016, Russian shipbuilding industry grew by 3% and military ship segment grew by 2.1% while productivity of civilian vessel construction reached 11.1%.
The most typical vessels built in 2016 include 2 diesel-electric submarines(Project 06363, Black Sea submarines), 1 submarine transferred to Vietnam(Project 06361), 2 Black Sea frigates, and a coast patrol vessel(Project 22100), etc. Among the vessels modernized and remodeled are included the aircraft carrier Admiral Kuznetsov and Ustinov missile cruiser. It is also known that 13 nuclear submarines, 5 diesel submarines, 20 frigates and 20 corvettes, and 2 large amphibious ships are also being remodeled.
In addition to the construction of the nuclear icebreaker, the construction of the offshore nuclear power plant is underway in Russia. Designing processes have been completed for the 70MW offshore power plant that can replace Chaunskaya cogeneration plant and Bilibino nuclear power plant in Chukotka region. 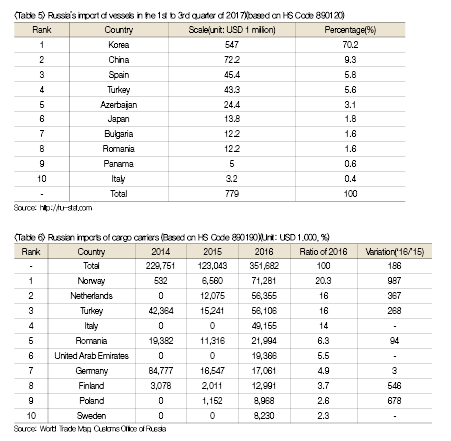
2. Trade of vessels in Russia
Russia’s ship imports range from USD 1 billion to USD1.1 billion per year, dominated by oil tankers and freighters. In the oil tanker(HS Code 890120) segment, vessels built by Korea comprise more than 70% in connection with the transfer of the icebreaker LNG carriers of Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering(DSME).
Cargo carriers(HS Code 890190) have been imported mainly from Europe, but the decreased drastically due to economic downturn and conflict with the West in 2015 before starting to recover from 2016. Those vessels are imported mainly from Norway, Netherlands, Turkey, Italy and Germany.
Russia’s annual exports of cargo carriers amount to USD 100 million to 200 million. Although Turkey is the main importer, Russia has exported more than USD 100 million worth of vessels to Japan. The vessels exported to Japan were found to be 2 units of cargo carriers based on the HS code.
3. Suggestions
Russia is currently proceeding with development of shipbuilding industry under the leadership of the government in three directions. So, now is the right time for technical cooperation between Korean companies and Russia. The first priority is to modernize shipyards based on investment in science and technology, the second priority is to replace the imported marine equipment, and the third priority is to expand exports of non-petroleum products based on development of shipbuilding industry.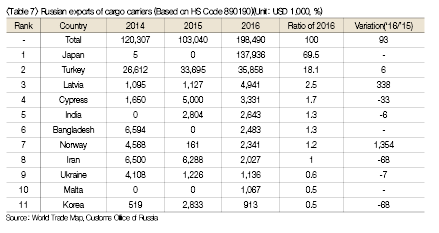
As Russia has world’s leading military fleet construction technology, Korea needs to increase technological cooperation with Russia, make investment in remodeling of military vessels based on delivery of marine equipment and help Russia achieve its ultimate goal of expanding the exports, thus creating the value-added. It is noteworthy that Russia, which has the world’s leading military fleet construction technology, has been recently exporting coastal cruisers and patrol submarines, remodeled from warships and submarines, to Algeria, Vietnam, and India.
Russia, which attracts attention globally for its industrial growth and Arctic route development in Arctic region, is taking comprehensive measures such as localization based on its policies designed to ensure balanced development of regions and development of manufacturing industry. Therefore, it would be necessary to participate actively in development projects suitable for the big pictures envisioned by policies of Russia. Since 2016, Russia has begun construction of icebreaker operating in the Ob river of Sabetta region for the Arctic development. Zvezda Shipyard established Zvezda Reduktor in St. Petersburg and has been developing the engine to replace Ukraine gas turbine. As of 2016, Russian shipbuilding industry comprised only 0.6% of the world’s shipbuilding industry, but the Russian government plans to raise the share to 3-5% by 2025.